IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Lower back pain - the causes of occurrence, in which diseases it occurs, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
Low back pain occurs in almost everyone, especially after 40 years. One of the reasons is osteochondrosis - a degenerative-dystrophic change in the spine. However, in many cases it does not explain the nature, severity and duration of back pain.
Varieties of pain
Back pain can be a symptom of a serious illness, but the vast majority of back pain is benign. One of the main points to consider when diagnosing back pain, and in particular in the lower back, is their duration. In most cases, muscle pain can last up to two weeks and then disappear. Pain caused by organic changes in the spine (intervertebral hernia, arthrosis) lasts much longer and can radiate to the leg, perineum, accompanied by a feeling of numbness, burning, goosebumps.
Pain caused by cardiovascular diseases, diseases of the abdominal organs are more intense and longer.
Possible reasons
Pain caused by disease or injury of the spine
In most cases, back pain is caused by dysfunction of the intervertebral joints.
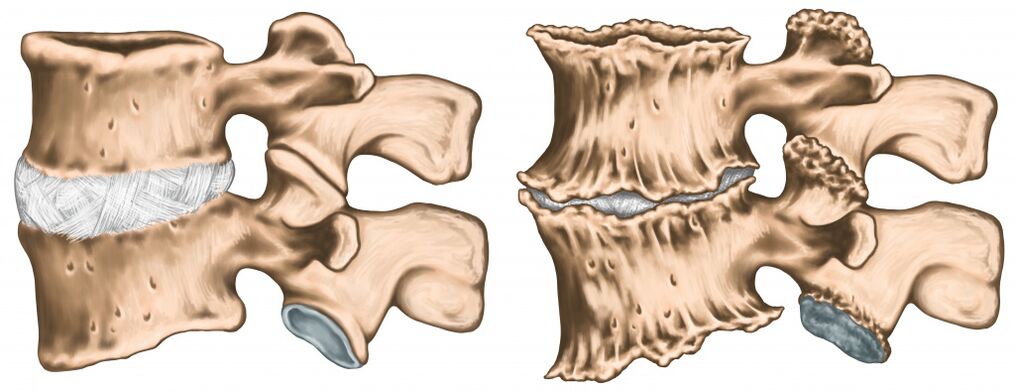
A decrease in the distance between the vertebrae due to degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs leads to an increase in the friction of the articular surfaces. This can cause subluxation and blockage of the joint. The muscles surrounding the affected joint are in a state of overexertion for a long time, which increases joint pain.
Most often, pain in diseases of the spine is dull in nature, i. e. , its intensity increases gradually, intensifying with movements and weakening at rest. .
In cases of severe osteochondrosis, pain can be caused by compression of the nerve endings (spinal roots) during the formation of a herniated disc. Sharp shooting or piercing pain can become constant over time and occasionally radiate to the leg with sudden movements, coughing, sneezing. The pain syndrome is usually accompanied by numbness, tingling, burning. Similar symptoms are combined with loss of sensitivity in the area of the affected nerve, loss of reflexes, muscle weakness.
Serious spinal injuries (fracture, fracture dislocation) are accompanied by severe pain and require emergency medical intervention.
If a fracture occurs as a result of compression of the vertebral body, then it is called a compression fracture.
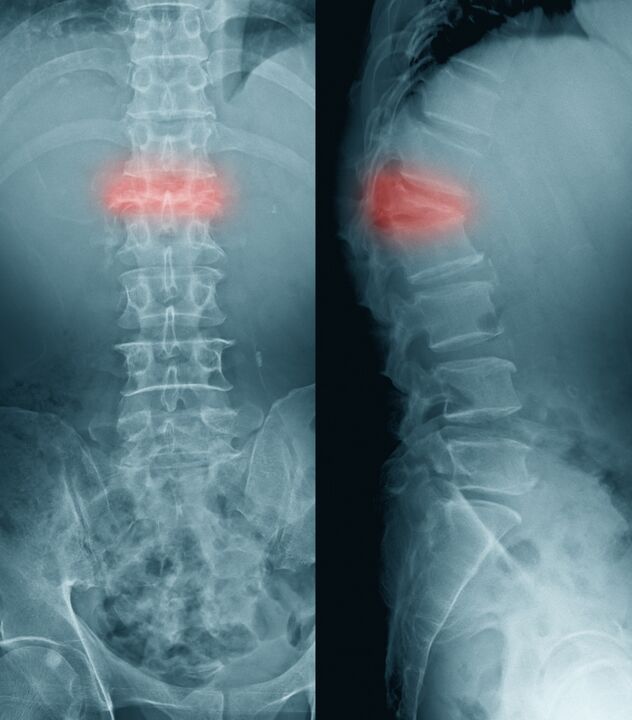
In older people, such a fracture is possible due to osteoporosis, which is more common in women. A compression fracture, sometimes even with minimal external load, is caused by damage to the spine during metastasis of malignant tumors.
Diagnostics and examinations
When diagnosing, the doctor takes into account orthopedic defects, the presence of symptoms such as impaired urination or defecation; pain spreading down the leg; lack of relief after taking painkillers; weakness and numbness in the leg. To confirm the diagnosis, you must perform:
- CT
- MRI
- Complete blood count One of the main laboratory tests for the quantitative and qualitative assessment of all classes of blood cells. Includes a cytological examination of a blood smear to calculate the percentage of leukocyte varieties and determine the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
What should be done when pain occurs?
In acute pain, it is necessary to ensure peace and limit the load on the spine.
In the presence of radicular syndrome, bed rest is observed for two weeks. After an acute period, you should gradually return to an active lifestyle.
Treatment
First of all, therapy should be aimed at relieving pain. The doctor may prescribe a blockade of the focus of inflammation with injections. Pain relief is achieved for a period of six weeks to six months. Another option is the appointment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in combination with muscle relaxants. Treatment can be supplemented with vitamin therapy (a complex of B vitamins), as well as the use of antidepressants and anticonvulsants strictly as directed. After the removal of acute pain, according to the decision of the doctor, thermal and magnetic physiotherapy, manual and acupuncture, massage can be added to the treatment.
If conservative treatment has proved ineffective for several months, neurosurgical operations are resorted to. At the age of 45, decompression of the spinal cord, removal of an intervertebral hernia, prosthetic intervertebral discs often give a good result. In other cases, it is better to use epidural blockade and radiofrequency denervation. This allows not only to quickly eliminate pain symptoms, but also to minimize the use of painkillers.
Muscle pain
Muscular, or myofascial, pain occurs most often with overstrain, spasm or microtrauma of the muscles.
In these cases, a painful and hard area of \u200b\u200bthe muscle is probed under the skin, pressing on which is accompanied by a strong pain impulse, and sometimes recoil to other areas. As a rule, there is a relationship between the occurrence of pain with prolonged overexertion or unnatural position (often associated with professional activities), compression and overstretching of muscles due to wearing heavy bags or backpacks, hypothermia, diseases of internal organs or joints. In the latter case, the pain impulse from the affected organ leads to a protective tension of the surrounding muscles.
Diagnostics and examinations
When making a diagnosis, the doctor conducts an external examination, finds out the history of the development of pain, its connection with overload or disease of the internal organs. To exclude damage to the spine (osteoporosis, metastases to the spine, tuberculous spondylitis):
- CT
- MRI
- Ultrasound to detect diseases of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis.
The absence of serious diseases of the spine and internal organs gives grounds for the diagnosis of myalgia, or muscle pain.
What should be done when pain occurs?
If the pain syndrome is due to muscle spasm, the first step should be to ensure rest and, if possible, relaxation.
The optimal effect is achieved in the supine position, preferably on an orthopedic mattress.
Treatment
The main therapy is to relieve pain and relax spasmodic muscles. This is achieved by the use of muscle relaxants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The course of treatment, on the recommendation of a doctor, can be supplemented with anticonvulsant drugs that reduce the intensity of pain, and vascular drugs that improve blood circulation in the muscles. The most effective conservative method is local injection blockade. After the removal of acute pain, it is possible to prescribe vitamins and biostimulants. Significant benefits are provided by non-pharmacological means: manual therapy, massage, acupuncture, physiotherapy, physiotherapy exercises.
Psychogenic pain
Psychogenic pain, as a rule, occurs without lesions and does not have a clear localization. Psychogenic pain develops as a response of the body to stressful situations and the negative emotions that accompany them. Unlike radicular or referred pain (when the localization of pain does not coincide with the focus of damage), psychogenic pain decreases or disappears after physical activity.
Psychogenic pain does not exclude a real organic lesion and even often accompanies its manifestations.
Diagnostics and examinations
It is quite difficult to identify the cause of psychogenic pain and determine its nature, especially in older patients. It is possible to suspect the psychological component of pain in the absence of its clear localization and nature, as well as in the presence of previous or current depressive states.
Treatment
The elimination of psychogenic pain is achieved by activating the lifestyle and using light tranquilizers and antidepressants as prescribed by the doctor.
Other possible causes of back pain
Other causes of pain syndromes can be infectious processes (tuberculous spondylitis, herpes), metastatic damage to the vertebrae, metabolic disorders (osteoporosis, hyperparathyroidism), vascular diseases (associated with vascular pathology), and lesions of internal organs. All of these conditions require urgent treatment.
Which doctors to contact?
Patients with back pain (if the pain is not of infectious or tumor origin) are treated by both general practitioners and neurologists, algologists, psychotherapists and exercise therapy doctors.